Defining B2B Sales: Examples and Strategies

B2B sales, short for "business-to-business" sales, constitutes the process of selling products or services from one business entity to another. In the realm of B2B sales, the customers are typically organizations or companies, as opposed to individual consumers.
The range of products or services involved in B2B sales can be quite diverse, serving either as integral components in the customer's business operations or as items for resale to their own clients. Given the complexity and involvement of multiple decision-makers and stakeholders in B2B sales, the establishment of strong client relationships and trust plays a pivotal role.
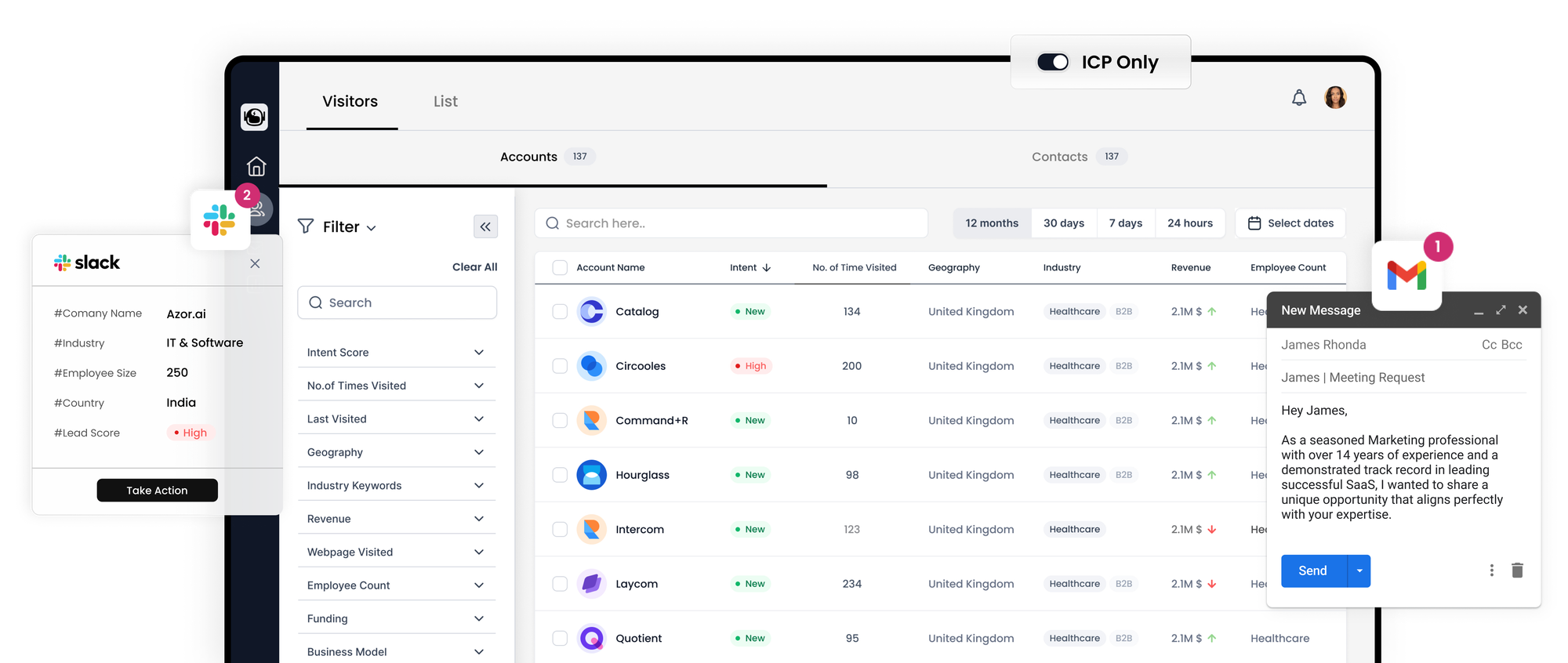
Distinguishing B2B Sales from B2C Sales:
B2B sales and B2C (business-to-consumer) sales are distinct approaches to marketing and selling products or services. Key distinctions between these two realms can be elaborated upon as follows:
1. Target Customers
- B2B sales primarily concentrates on selling to other businesses and enterprises.
- B2C sales, conversely, revolves around selling directly to individual consumers.
2. Sales Strategies
- B2B sales often adopts a consultative approach, tailoring customized solutions, and emphasizing ongoing account management to foster enduring customer relationships.
- In contrast, B2C sales is typically more transactional, prioritizing the satisfaction of individual customer desires and needs.
3. Sales Cycles
- B2B sales typically entails a lengthier sales cycle due to the involvement of a group of decision-makers and more intricate requirements.
- B2C sales, on the other hand, tends to feature shorter and more straightforward sales cycles.
4. Transactions
- B2C sales frequently encompass high-volume, lower-value transactions.
- B2B sales, conversely, typically revolves around fewer, yet higher-value transactions.
5. Marketing Tactics
- B2B marketing strategies often include targeted advertising, content marketing, and relationship cultivation to establish the company as a trusted industry authority.
- B2C marketing frequently employs emotional appeals, brand recognition, and price promotions to attract and retain individual consumers.
Illustrations of B2B Sales:
To further elucidate the concept of B2B sales, consider the following examples:
1. Tire Casing Manufacturers
These businesses manufacture tire casings and sell them to automobile manufacturers, which then use these components to assemble vehicles.
2. Supermarkets
Supermarkets engage in B2B sales by procuring products from suppliers at wholesale prices and subsequently reselling these items at retail prices to individual consumers.
3. Law Firms
Legal firms often specialize in B2B sales when they take on corporate cases or provide legal services to businesses.
4. Marketing Agencies
Marketing agencies engage in B2B sales as they collaborate with companies to devise marketing strategies and create content for branding and promotional purposes.
In essence, any service provider or supplier that offers its services to other companies or organizations falls within the realm of B2B sales.
Defining the Role of a B2B Sales Representative and Delving into B2B Sales Strategy
A B2B sales representative, also referred to as a "sales rep," is a pivotal customer-facing professional who actively seeks out and establishes relationships with decision-makers within corporate entities. Their primary objective is to promote and sell the solutions offered by their company, thereby directly contributing to the development of inter-organizational relationships, portfolio expansion, and revenue generation.
Guided by a well-defined playbook based on the company's sales process, B2B sales representatives employ a diverse array of professional sales skills, techniques, and tools. Their ultimate aim is to cultivate trust and long-lasting connections with potential buyers while offering tailored solutions that align with the buyers' specific needs.
The daily responsibilities of a typical B2B sales representative encompass a wide spectrum of tasks, including:
1. Generating Profit
This involves not only identifying new prospective customers but also retaining existing ones. Sales reps educate potential buyers about the advantages of the products or services offered, provide comprehensive customer support, oversee online transactions and sales, and work diligently to achieve volume and margin sales targets on a weekly, quarterly, monthly, and annual basis.
2. Building Strong Customer Relationships
B2B sales reps prioritize the cultivation of robust relationships with key customer accounts. This ensures a high level of service quality and fosters customer loyalty.
3. Financial Transactions
Sales reps facilitate financial dealings by offering customers estimated budgets, establishing payment agreements, and providing delivery estimates. They may also draft contracts, manage pricing structures, compile sales data and activity reports, solicit purchase orders, and conduct post-sale follow-ups.
4. Reporting
Regularly generating reports based on sales data and performance metrics is an essential aspect of the role. These reports aid in decision-making and strategy refinement.
5. Administrative Duties
Sales representatives often perform various administrative tasks, which can include managing documentation, organizing schedules, and coordinating logistics.
6. Market Awareness
Staying abreast of current market trends and industry developments is crucial for a B2B sales rep to remain effective in their role.
7. Team Oversight
In some instances, B2B sales representatives may monitor and supervise the activities of other members within the sales team, ensuring alignment with organizational goals.
B2B Sales Strategy:
B2B sales presents a unique set of challenges and considerations due to the distinct nature of corporate customers and their demands. Several key parameters significantly influence B2B sales strategies:
1. Industry Focus
The specific industry in which a B2B company operates plays a critical role in shaping its sales strategy. Understanding industry-specific dynamics and requirements is essential for success.
2. Product Offerings
The type of product or service a company provides directly impacts its sales approach. Sales reps must tailor their strategies to effectively communicate the value and benefits of the offerings.
3. Sales Channels
The channels through which a company delivers its products or services to the market are instrumental in determining the sales strategy. These channels may include direct sales, distribution partners, online platforms, and more.
In B2B sales, salespeople must adeptly navigate interactions with various departments within a buyer's organization. From administrators and secretaries to assistants and managers, different professionals may participate in the purchasing process. Each individual may focus on distinct aspects of the product, such as price, advantages, and additional incentives.
B2B sales often entails a narrower potential market and a more intricate sales cycle compared to B2C sales. While the process may be more complex, it can also elevate a company to a higher level of success. Consequently, some companies opt to simultaneously engage with both B2B and B2C clients, leveraging the strengths of each approach to maximize their reach and impact.
Exploring the B2B Sales Process: Phases and Significance
The B2B sales process encompasses a structured sequence of actions and stages involved in the sale of products or services from one business to another. While the specifics of this process can vary depending on factors such as industry and the nature of the offering, certain fundamental steps are generally present in most B2B sales procedures. These steps collectively serve as a roadmap for businesses to effectively market their products or services to other businesses while fostering enduring customer relationships.
Key Phases of the B2B Sales Process:
B2B sales is a sophisticated endeavor that necessitates meticulous planning, thoughtful strategy formulation, and skillful execution to achieve success. It unfolds in a series of well-defined stages, actions, and events, often requiring the application of diverse sales methodologies tailored to different buyer profiles and scenarios.
The number of stages within the B2B sales process can vary based on industry dynamics and organizational characteristics, typically comprising a sales cycle spanning 5 to 8 stages:
1. Prospecting
The initial stage of B2B sales, prospecting, involves comprehensive market research to identify potential leads and decision-makers within target organizations. By conducting market research, sales professionals gain insights to focus their efforts effectively. Identifying key decision-makers enables concentrated engagement with individuals capable of authorizing purchases. The creation of a lead database facilitates ongoing interaction tracking, pivotal for propelling the sales process forward. In essence, prospecting lays the groundwork for subsequent stages in the B2B sales journey.
2. Qualifying
Following prospecting, the next phase involves lead qualification, whereby generated leads are evaluated to determine their potential as future customers. Qualification entails assessing the prospective customer's needs, budget constraints, timeline, and decision-making process. Gaining an understanding of the customer's needs empowers sales professionals to position their product or service as a viable solution. Budget considerations help determine affordability and potential negotiation points. Awareness of the timeline provides insights into decision timing and potential delays. Knowledge of the decision-making process informs a tailored approach that resonates with key decision-makers. Ultimately, lead qualification aids in prioritizing efforts and increasing the likelihood of successful conversions.
3. Needs Assessment
Once a lead is qualified, the subsequent step involves conducting a comprehensive needs assessment. This phase centers on gathering specific information concerning the customer's needs and requirements, with a focus on demonstrating how the offered product or service can effectively address those needs. Effective needs assessment demands the ability to pose pertinent questions, actively listen to the customer, and tailor the sales pitch to showcase how the solution aligns with the customer's requirements. This stage is pivotal for building trust and nurturing customer relationships, positioning sales professionals as valuable partners and enhancing the likelihood of closing the sale.
4. Presentation
The presentation phase marks a critical juncture in the B2B sales process. Here, sales professionals emphasize why their solution is the optimal choice for the customer. By highlighting the benefits and features of their product or service, customized to suit the customer's specific needs, they aim to address pain points and furnish tangible examples of how their offering can deliver value. Sales representatives must be well-prepared to address any queries from the customer regarding the products or services and provide responses that are both confident and informative.
5. Handling Objections
In this stage, sales professionals proactively engage with any customer concerns or objections that may arise during the presentation. They actively listen to the customer's perspective, offering reassurance or additional information to address objections and foster trust. Effectively handling objections necessitates proficiency, confidence, and conciseness in communication. Skillful execution at this stage significantly bolsters the likelihood of closing the deal.
6. Closing
When the customer expresses satisfaction with the offered product or service, the salesperson proceeds to close the sale. This phase entails negotiating the terms of the sale, encompassing aspects such as price, delivery arrangements, and payment terms. Achieving a mutually acceptable price point, offering flexible payment and delivery options, and addressing any remaining concerns or objections from the customer are key elements of successful closing. Formalizing the purchase agreement through the creation of contracts or legal documentation is often a requisite step in this stage. Effective closing demands adept persuasion, negotiation, and communication skills.
7. Follow-Up
The follow-up stage constitutes a vital aspect of the B2B sales process, occurring after the sale has been finalized. Its primary objectives are to ensure customer satisfaction and promptly address any post-sale issues that may arise. Maintaining ongoing communication with the customer plays a pivotal role in nurturing long-term relationships that can translate into repeat business and revenue growth.
8. Check-In
After a prospect transitions into a client, the check-in stage comes into play. Its purpose is to maintain ongoing communication with the client, ensuring their ongoing satisfaction and addressing any outstanding concerns or issues. Prioritizing these aspects enables sales professionals to cultivate robust, enduring relationships conducive to repeat business and revenue expansion.
In summary, the B2B sales process entails a meticulously choreographed sequence of stages, each of which plays a critical role in building productive customer relationships and achieving successful sales outcomes. Adaptation and fine-tuning of these stages to align with specific industry contexts and customer profiles are essential for sustained success in B2B sales endeavors.
